Introduction
A variable is a labeled container that stores information in your workflow or chatflow. Each variable holds a piece of data—whether it’s user input, system-generated values, or outputs from previous nodes. When you need to use this information later, you simply reference it by its name. When building a workflow or chatflow, you’ll work with different types of variables, each serving a specific purpose in your application’s data flow.Variable Types
System Variable
System variables are pre-set, system-level parameters that are globally available.- Workflow
- Chatflow
| Variable Name | Data Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
sys.user_id | String | User ID: A unique identifier automatically assigned by the system to each user when they use a workflow application. It is used to distinguish different users. | |
sys.app_id | String | App ID: A unique identifier automatically assigned by the system to each App. This parameter is used to record the basic information of the current application. | This parameter is used to differentiate and locate distinct Workflow applications for users with development capabilities. |
sys.workflow_id | String | Workflow ID: This parameter records information about all nodes information in the current Workflow application. | This parameter can be used by users with development capabilities to track and record information about the nodes contained within a Workflow. |
sys.workflow_run_id | String | Workflow Run ID: Used to record the runtime status and execution logs of a Workflow application. | This parameter can be used by users with development capabilities to track the application’s historical execution records. |
sys.timestamp | String | The start time of each workflow execution. |
Environment Variables
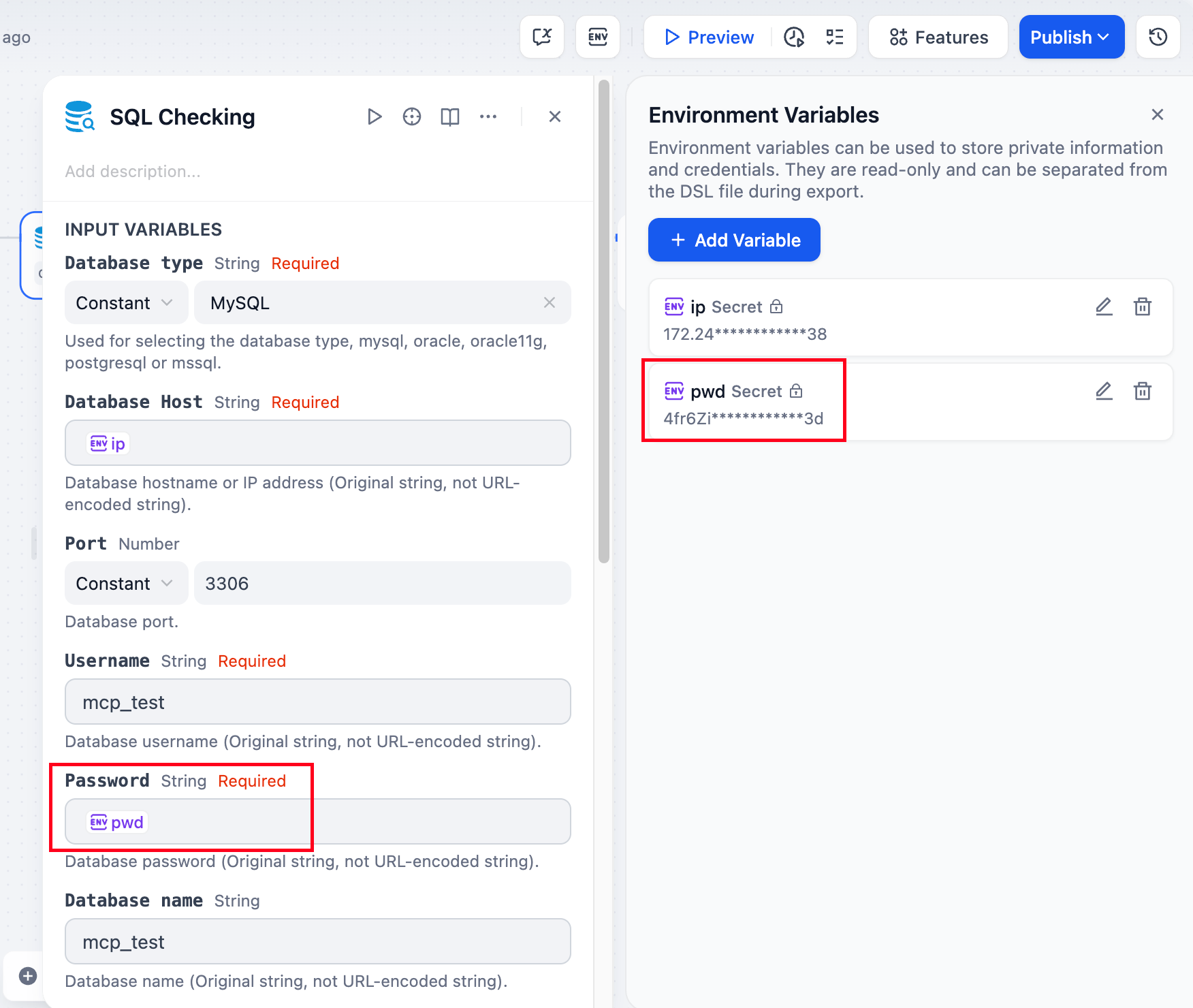
Environment variables are used to protect sensitive information involved in workflows, such as API keys and database passwords used when running workflows. They are stored in the workflow rather than in the code, allowing them to be shared across different environments.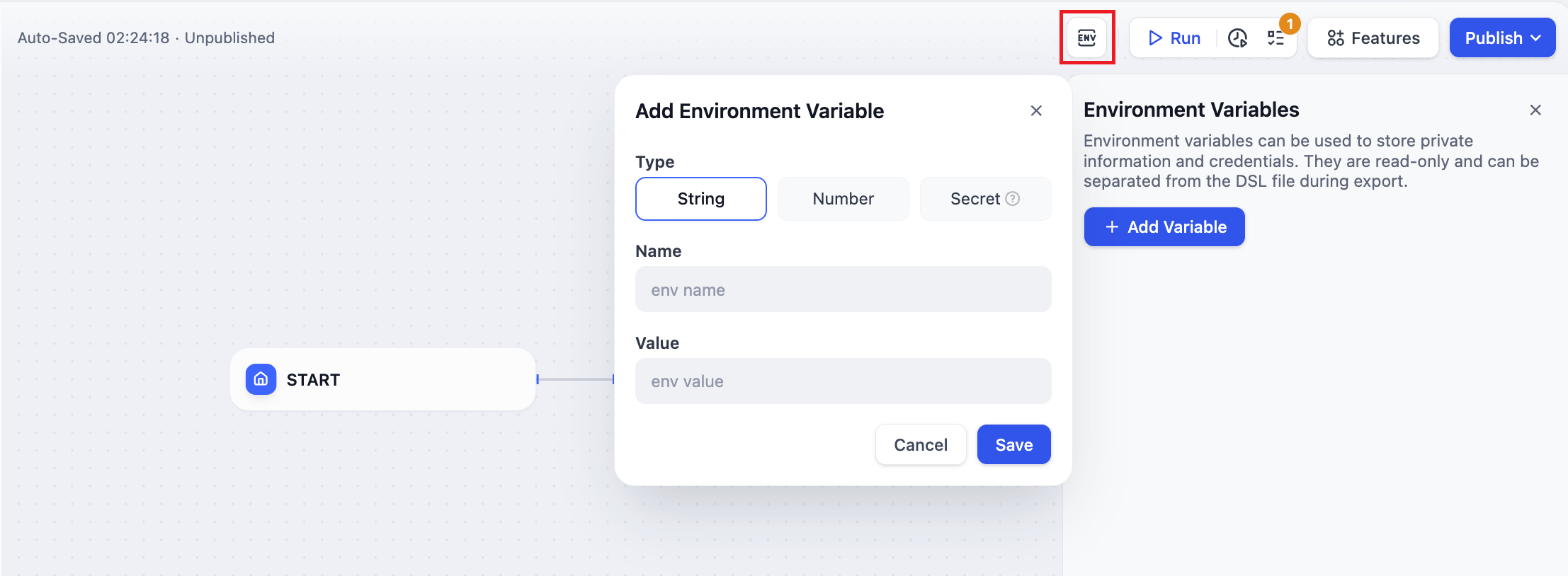 Supports the following 3 data types:
Supports the following 3 data types:
- String
- Number
- Secret
- Environment variables can be globally referenced within most nodes;
- Environment variable names cannot be duplicated;
- Output variables of nodes are generally read-only and cannot be written to.
Conversation Variables
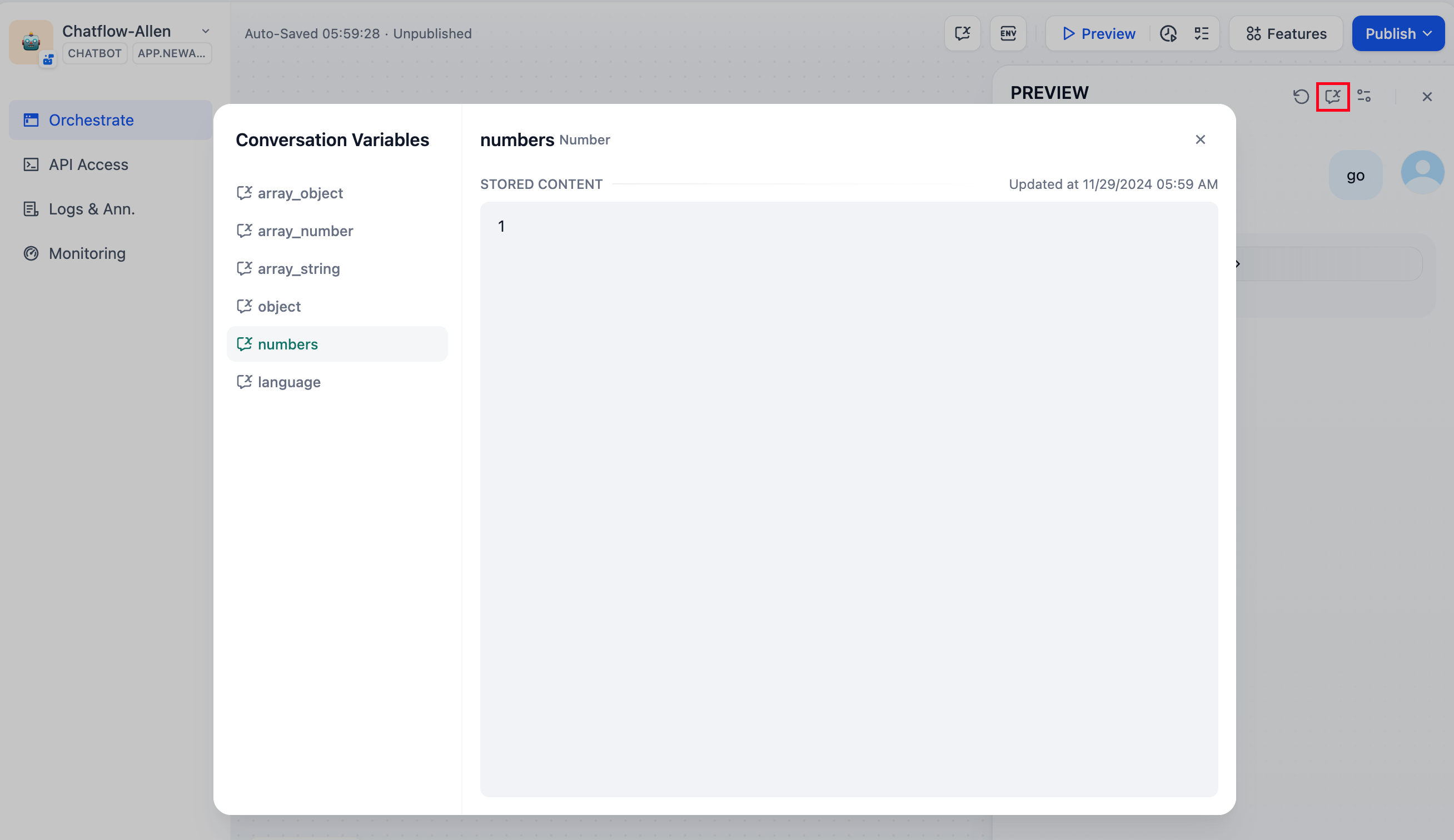
Conversation variables are only applicable to Chatflow App.Conversation variables allow application developers to specify particular information that needs to be temporarily stored within the same Chatflow session, ensuring that this information can be referenced across multiple rounds of chatting within the current chatflow. This can include context, files uploaded to the chatting box(coming soon), user preferences input during the conversation, etc. It’s like providing a “memo” for the LLM that can be checked at any time, avoiding information bias caused by LLM memory errors. For example, you can store the language preference input by the user in the first round of chatting in a conversation variable. The LLM will refer to the information in the conversation variable when answering and use the specified language to reply to the user in subsequent chats.
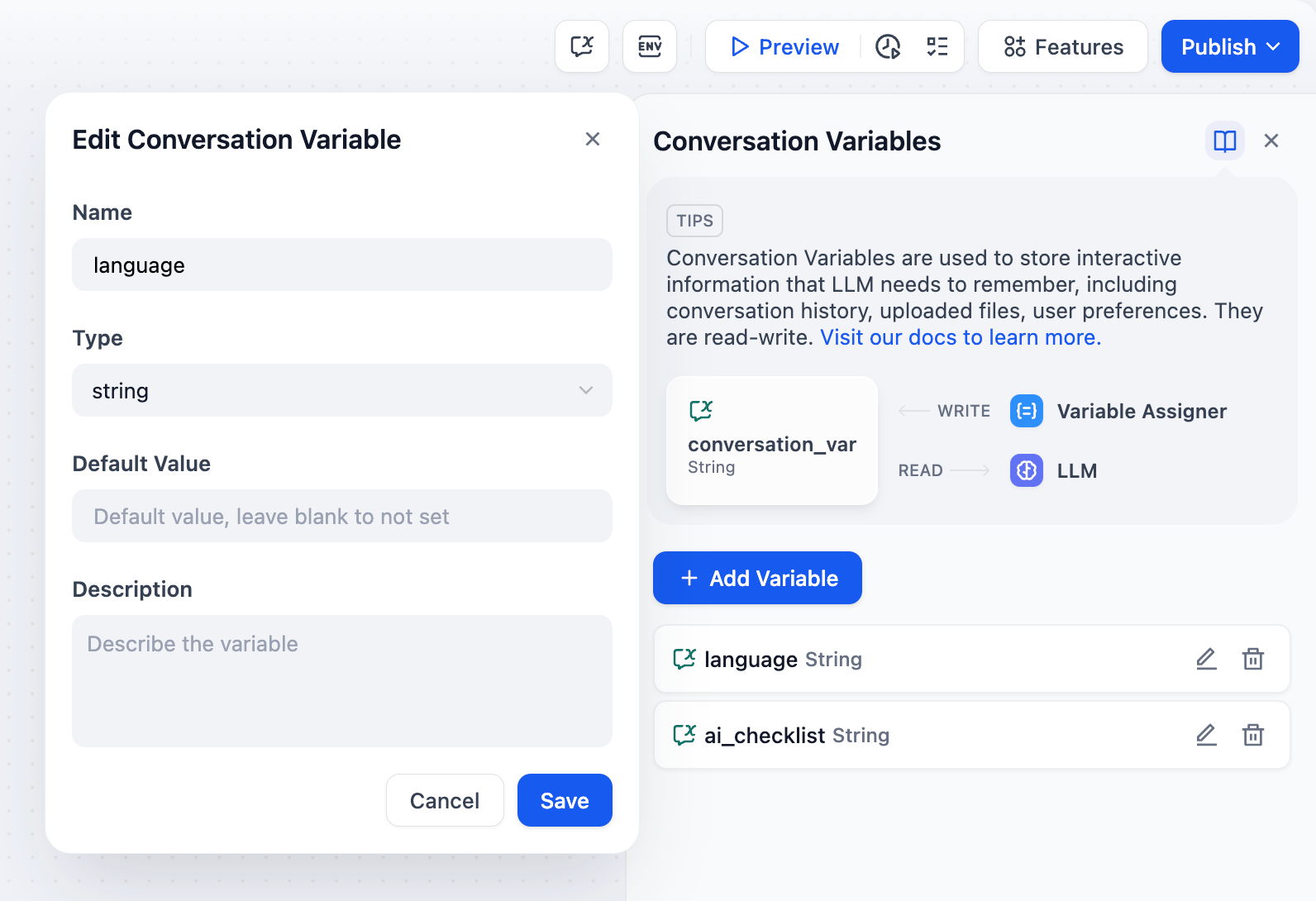 Conversation variables support the following eight data types:
Conversation variables support the following eight data types:
- String
- Number
- Object
- Boolean
- Array[string]
- Array[number]
- Array[object]
- Array[boolean]
- Conversation variables can be referenced globally within most nodes in the same Chatflow App;
- Writing to conversation variables requires using the Variable Assigner node;
- Conversation variables are read-write variables;
Notice
- To avoid variable name duplication, node naming must not be repeated
- The output variables of nodes are generally fixed variables and cannot be edited
Edit this page | Report an issue

